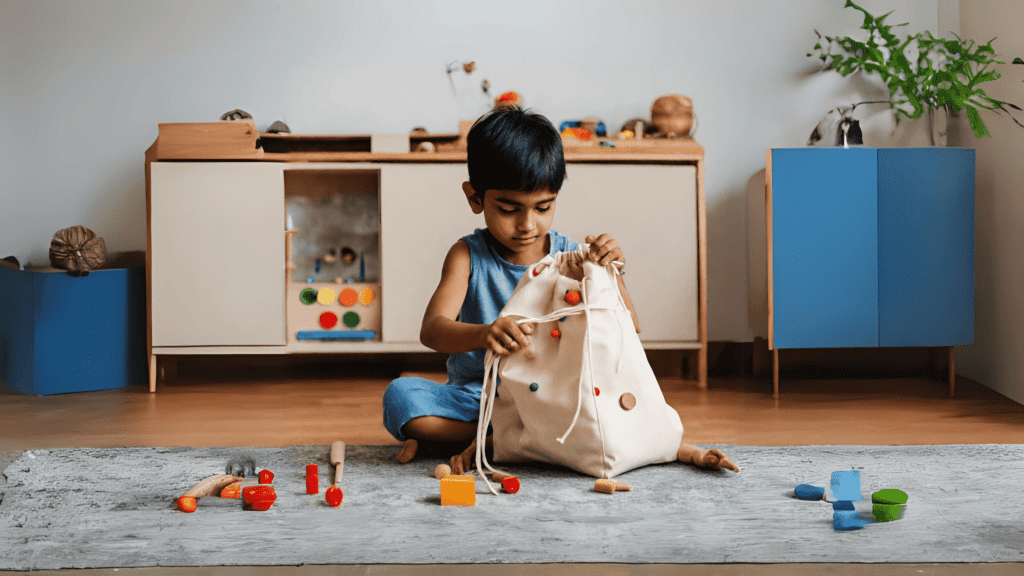
The sensory section of the Montessori Method includes the stereognostic bag exercise. This activity is intended for children ages 3 to 5.
The Montessori Method includes “sensorial stimulation” as a major component of the curriculum. It is intended to give the children the essential stimuli to pique their curiosity. According to the Montessori Method of Education, the ability to determine an assigned object’s texture, shape, spatial properties, and consistency only through tactile information—without having to see, hear, or even smell it—is known as the stereognostic sense.
To help children develop their stereognostic sense, the Montessori Method of education uses inventive and intuitive activities.
What Exactly Is Stereognostic Sense ?
According to the Montessori curriculum, the “sixth” sense is the stereognostic sense. In simple terms, it is the fusion of tactile and muscle memory.
This sense is also known as Tactile Gnosis. It is the capacity to identify and recognize objects based only on tactile information. A child who possesses this ability will not be able to identify the object using their spatial, hearing, sensory, or olfactory senses.
The child’s other senses, particularly their tactile senses, are enhanced and developed by the stereognostic sense.
What is a Stereognostic Bag?
A stereognostic bag, also called a mystery bag or touch bag, is a type of sensory aid that is used in Montessori education to improve cognitive skills and tactile perception. A bag or container is filled with different objects that the children can feel with their hands but cannot see.
The objective is to use only touch perception and memory to identify and recognize the objects.
What are the Benefits Of Stereognostic Sense?
There are numerous advantages to developing the stereognostic sense.
- It helps the child distinguish and discriminate between various shapes, structures and sizes even without seeing them.
- The child can quickly distinguish between two different stimuli that are close together.
- The child can effectively use their tactile senses to discriminate between environmental stressors.
- The stereognostic sense helps the child to visualise by forming mental images.
Presentation Of Stereognostic Bag/ Mystery Bag Activity
Material Required
- A cloth bag with a drawstring
-
A selection of Montessori sensorial objects. These are everyday objects with distinct textures, shapes, sizes, temperatures, or weights.
- Examples: Wooden geometric solids, smooth stones, pinecones, soft fabric scraps, metal spoons, etc.
How to Introduce Montessori Mystery Bag Activity to the Children?
- Selection: Carefully choose a set of sensorial objects that vary in their properties. Ensure all objects are safe for children to touch.
- Demonstration: Show the child the empty bag and explain it’s a mystery bag. Place one object from your selection inside and close the bag.
- Exploration: Invite the child to reach into the bag with one hand, feel the object, and describe its characteristics (bumpy, cold, round, etc.). Encourage them to guess what it might be.
- Reveal: After some exploration and guesses, help the child take the object out and see if their guess was correct. Also, say the name out loud: i.e. “I think this is a cotton ball.”
- Exploration and Discussion: Let the child freely explore the object visually and continue describing its properties. You can also discuss how the object might be used in daily life.
- Repeat: Place another object in the bag and repeat the exploration process.
- Invitation: Invite the children to try this activity.
Tips to Present
Here are some tips to make the introduction of the stereognostic bag enjoyable and beneficial.
- Create excitement with presenting the bag as a surprise or mystery.
- Select the age-appropriate objects with different shapes, textures, and sizes.
- Show the children how to explore the bag by reaching in without looking.
- Use descriptive language to explain how they can identify objects by feeling their shape, texture, and size.
- Let children take turns reaching into the bag and identifying objects.
- Turn the activity into a game by challenging them to guess the object or find a specific one based on your description or clues they discover through touch.
Activities for Stereognostic Bag
By making the introduction to the stereognostic bag interactive, playful, and supportive, children are likely to engage more enthusiastically in this sensory activity while enhancing their tactile discrimination skills and vocabulary. Here are some activities for the introduction of this sensory bag.
- Place a set of shapes inside the bag and the other set of shapes on the table. Touch and feel one of the shapes on the table, then use your Stereognostic sense to find a similar shape inside the bag. Place the shape next to its pair and continue with the next shape.
- Introduce mystery items in the bag. Participants take turns feeling an item and describing it without revealing what it is. Others guess the object based on the description.
- Include objects with various textures (smooth, rough, soft, hard) in the bag. Children can explore and discuss the textures they feel, aiding sensory awareness and vocabulary.
Montessori Twist:
- Pairing Objects: Introduce the concept of matching by placing two identical objects in the bag. The child can reach in, find both, and then visually confirm the match.
- Geometric Focus: Use the mystery bag activity to reinforce geometric shapes learned through Montessori materials like geometric solids.
Notes
This stereognostic bag activity can be done with varied small and medium sized objects. Change the objects while working in a group of children. This would help them visualise and feel varied shapes and sizes.
By incorporating the Montessori mystery bag activity into your child’s routine, you’ll be providing them with a fun and enriching sensory experience that aligns perfectly with Montessori principles of independent learning and exploration.